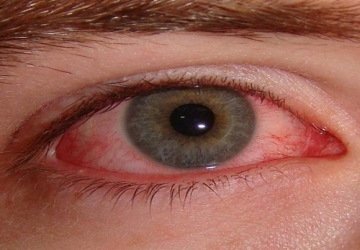
veitis is a type of inflammation that affects the eye, as the iris is known as one of the parts of the middle layer of the eye known as the uvea.
Symptoms and signs of uveitis
With the question of Dr. Muhammad Hantira, an honorary assistant professor, ophthalmology department, Umm Al-Qura University, Saudi Arabia
Explain that there are many symptoms associated with uveitis, including:
•Severe eye pain when exposed to bright light.
• Low vision or blurred vision.
•Pain in the eyes and eyebrow area.
•Redness, especially around the iris.
•Change in the shape or size of the pupil.
•a headache.
Causes of uveitis
Dr. Hantereh explained
Uveitis occurs for unknown reasons, and in these cases the inflammation appears only once.
But many causes may contribute to uveitis, and most of the time the inflammation occurs repeatedly, as the causes of uveitis include the following:
•Eye injury.
•Inflammation of eye surgery.
•Infections such as tuberculosis virus, herpes virus, and others.
•Sarcoidosis.
•Behçet's disease (Adamantiades-Behçet's disease).
• The use of some medications, such as those used to treat glaucoma.
•Autoimmune diseases, such as seborrheic fever and rheumatoid arthritis.
Risk factors for uveitis
Dr. Hantereh indicated:
There are many factors that increase the risk of developing uveitis, as these factors include the following:
•Smoking. Smoking increases the risk of developing iritis.
• Having a sexually transmitted infection, such as AIDS.
•Immune disorders or a weakened immune system.
•Genetic changes.
Diagnosing uveitis
Dr. Hantira explained:
An ophthalmologist diagnoses uveitis, who performs a complete eye examination, and this examination includes the following:
•External examination of the eye.
•Slit lamp examination.
•Visual acuity test.
Treating uveitis
Dr. Hantereh noted:
It is imperative to begin treatment for uveitis immediately upon confirmation of the diagnosis, and it may require more than one follow-up visit to the doctor to finish the treatment.
It is worth noting that there are some medical treatments used for uveitis, which include the following:
•Steroid: Steroid is used to reduce inflammation, as the doctor begins by prescribing steroid eye drops, and if the patient does not respond within a week of treatment with them, he can prescribe pills or needles.
•Eye drops: Eye drops are used to treat uveitis, to help dilate the pupil and prevent contractions.
•Antibiotic or viral: In cases of bacterial infection, antibiotics and antivirals are used in the event of viral infections in the iris.
• Anticholinergic drugs: Anticholinergics reduce pain and light sensitivity by blocking the nerve signals for each.
Prevention methods for uveitis
Dr. Hantereh indicated:
Noting that there are many methods used to prevent uveitis, as these methods include the following:
• Avoid practices that increase the risk of developing iritis, such as smoking.
•Protect the eye from injuries.
•Reducing the eye's exposure to infection.
•Eat healthy diets rich in vitamins, such as vitamin C.
•Do a stress-free exercise, such as yoga.